
Moreover, it is largely unknown whether one of the MELD scores or its 3 modifications is superior for predicting the risk of mortality.Īccordingly, we aimed to assess the prognostic role of the MELD_albumin score in patients with AHF over a long-term follow-up. However, the prognostic value of the MELD including albumin (MELD_albumin) score, which includes the serum value of albumin rather than the international normalized ratio, in AHF patients is still unknown. Several studies also focused on the effects of modified MELD versions, such as the MELD excluding the international normalized ratio (MELD_XI) score, and the MELD including sodium (MELD_sodium) score, on the prognosis of acute heart failure. The model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score evaluating liver and renal function was considered a reliable predictor for the risk of adverse events in AHF patients. Biomarkers that reflect liver and kidney function are often used to predict adverse clinical outcomes in patients with AHF. In that sense, simple score capable of quantitating the severity of multiorgan failure is attractive. Complicated interaction between heart, kidney, and liver has been an object of interest for a long time. Liver and renal dysfunction are often complicated in patients with acute heart failure. The predominant clinical profile in most patients with AHF is congestion and hypoperfusion, which can lead to organ dysfunction and increase the risk of mortality.

Acute heart failure (AHF) is a complex syndrome characterized by worsening heart failure symptoms. With the increase in HF patients, HF has recently become a serious health problem. Heart failure (HF) is a common disease and is associated with considerable morbidity and mortality worldwide. The MELD_albumin score increases risk stratification of all-cause mortality over and beyond the MELD score and the other modified MELD scores in patients with acute heart failure. Considering reclassification, MELD_albumin score increased the net reclassification improvement over and beyond MELD (13.1%, P = 0.003), MELD_XI (14.8%, P = 0.002), and MELD_sodium (11.9%, P = 0.006) scores for all-cause mortality. The MELD_albumin score showed the best prognostic accuracy (AUC = 0.658) for the prediction of long-term all-cause mortality, followed by the MELD_sodium score (AUC = 0.590), the MELD score (AUC = 0.580), and the MELD_XI score (AUC = 0.544) the MELD_albumin score performs significantly more accurate than MELD and MELD_XI score for predicting the risk of all-cause mortality. In the fully adjusted Cox regression model, standardized hazard ratios with 95% confidence interval expressing the risk of all-cause mortality were 1.22 (1.06–1.40), 1.20 (1.04–1.39), 1.23 (1.06–1.42) and 1.21 (1.05–1.41) for MELD, MELD_XI, MELD_sodium and MELD_albumin scores, respectively. Resultsĭuring a median follow-up period of 34 months, 196 deaths occurred. We compared the accuracy of the 4 MELD score formulas using the time-dependent receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and corresponding areas under the curve (AUC).
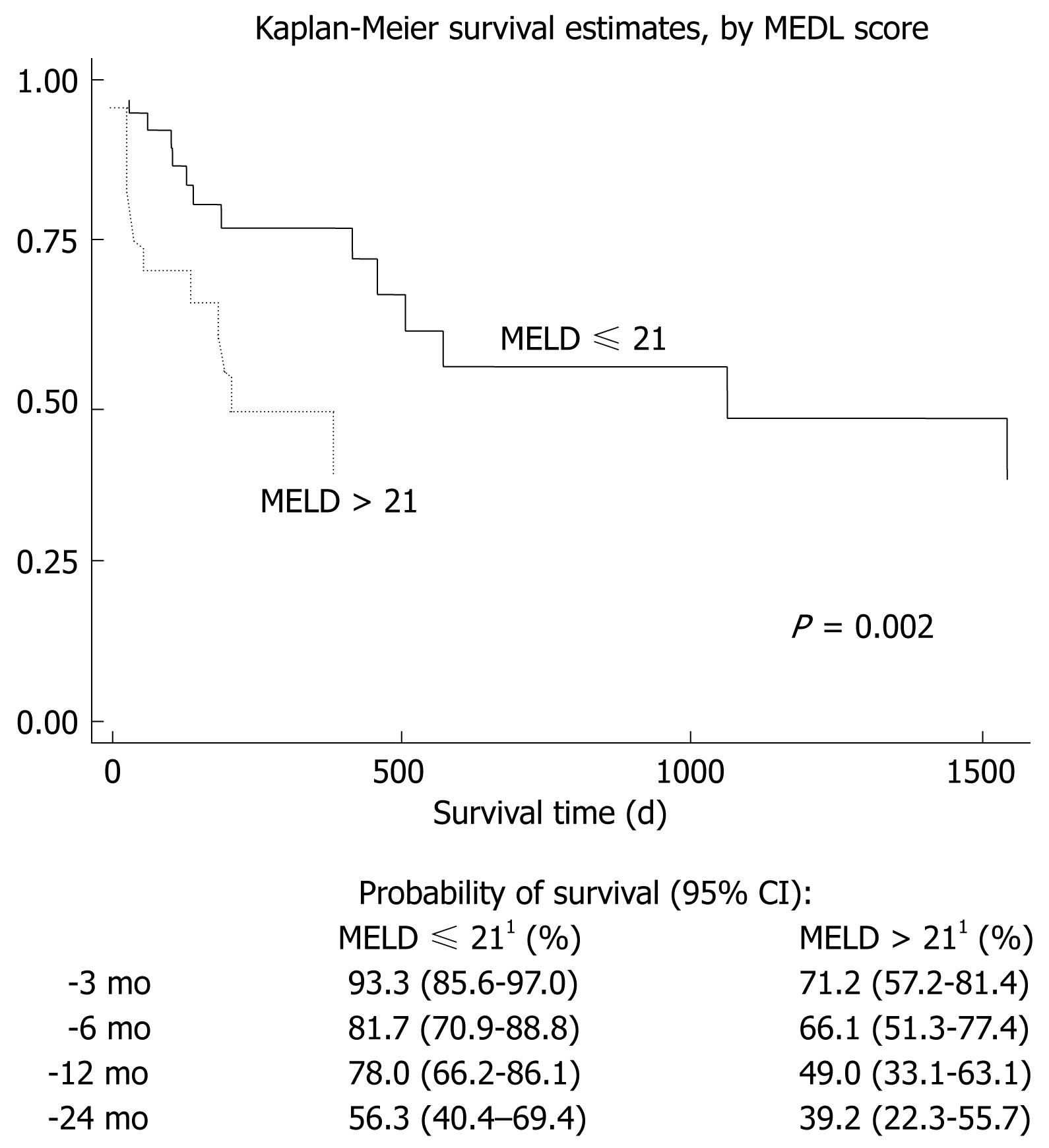
MethodsĪ total of 466 patients with AHF were prospectively evaluated. However, the prognostic value of the MELD including albumin (MELD_albumin) score in patients with AHF has not been assessed. Liver and renal function evaluated by the model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score, the MELD excluding the international normalized ratio (MELD_XI) score and the MELD including sodium (MELD_sodium) score have been considered predictors of adverse events for patients with acute heart failure (AHF).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
